Day 1
👋
Welcome!

Daniel Kelly
Lead Instructor @ Vue School
Full Stack developer (10 years)
Husband and Father
presentation Icons from fontawesome.com
Nuxt 2 → Nuxt 3
Workshop

Intro
What's New in Nuxt 3
1
Vue

Vue
Dynamic/Reactive Frontends
<template>
<div>
<h1>Nuxt is Awesome!</h1>
<ul v-auto-animate>
<li
v-for="reason in soManyReasons"
:key="reason">
{{ reason }}
</li>
</ul>
</div>
</template>Templating

v2
Vue

3
Vue

3

Increased Performance
- ~55% faster overall
- updates up to 33% faster
- memory usage ⬇ 54%
TypeScript Support
- Improved DX
- Zero-config
- Less fragile apps

Composition API
- Better logic reuse
- Flexible code organization
- Better type inference

v3
Vue

3
Composition API
- Better logic reuse
- Flexible code organization
- Better type inference

v3
Game Changer
Vue

3
Composition API
- Better logic reuse
- Flexible code organization
- Better type inference

v3
You can write your own reusable composables to extract logic
Vue

3
Composition API
- Better logic reuse
- Flexible code organization
- Better type inference

v3
Or reach for off the shelf composables

VueUse
pre-installed in our exercise project and we'll use it a bit later in an exercise
Universal Rendering



Better Performance
No waiting for browser to
run JS app and render
Improved SEO
Web crawlers directly index
the page's content
Universal Rendering
Static Site Generation
Cheap, fast, secure hosting
on the Jamstack


v2


Better Performance
No waiting for browser to
run JS app and render
Improved SEO
Web crawlers directly index
the page's content
Universal Rendering
Static Site Generation
Cheap, fast, secure hosting
on the Jamstack


New and Improved
💪

Runs Anywhere
Not just Node anymore.
Deno, workers, +
Built for Fast
Cold Starts
Great for serving from
Lambda or Edge Functions
Universal Rendering
Hybrid Rendering
Support multiple
rendering modes on a
single app


v3
Thanks to Nitro
⚗️
https://nitro.unjs.io/
Framework agnostic server engine
Thanks to Nitro
⚗️
Tons of features!

Thanks to Nitro
⚗️
Tons of features!
Thanks to Nitro
⚗️
internally uses h3 for mapping requests to handlers
Nuxt
Nitro
h3
Thanks to Nitro
⚗️
Most exciting features to me include:
Hybrid Rendering
Universal Deploys
Hybrid Rendering

export default defineNuxtConfig({
routeRules: {
// Static page generated on-demand, revalidates in background
'/blog/**': { swr: true },
// Static page generated on-demand once
'/articles/**': { static: true },
// Set custom headers matching paths
'/_nuxt/**': { headers: { 'cache-control': 's-maxage=0' } },
// Render these routes with SPA
'/admin/**': { ssr: false },
// Add cors headers
'/api/v1/**': { cors: true },
// Add redirect headers
'/old-page': { redirect: '/new-page' },
'/old-page2': { redirect: { to: '/new-page', statusCode: 302 } }
}
})
v3
Hybrid Rendering

- ssr: false - admin dashboards, SaaS apps, etc when SEO isn't important
- static: true - marketing pages, blog posts, etc
- swr: true - any page with dynamic content that changes semi-often
Hybrid Rendering

v3
Zero-Config Deploys
Or minimal config deploys
v3













Tooling

Webpack
Bundling and
development server
with HMR
CLI
Start dev server, build for production, ssg


v2

Tooling
Vite
Lightning fast
development server
with HMR
Nuxi CLI
Everything from Nuxt CLI
plus: file scaffolding, updates,
cleanup, and more!


v3

Tooling
Nuxt Devtools
set of visual tools to
help you better understand
your app
more on this in a bit

v3

Tooling
npx nuxi add page HelloWorld// @/pages/HelloWorld.vue
<script lang="ts" setup></script>
<template>
<div>
Page: foo
</div>
</template>
<style scoped></style>
Nuxi CLI
v3

Tooling
npx nuxi add plugin MyPlugin// @/plugins/MyPlugin.ts
export default defineNuxtPlugin((nuxtApp) => {})
Nuxi CLI
Questions?
🙋
Exercise
1
Coffee Break
☕️
15 mins
File Structure
2
And how syntax has changed
File Structure

Conventions
Predictable file structure
that's easy to navigate
Functionality Based
on Directory
Auto imported components,
file-based routing, etc

v2
File Structure

Conventions
Predictable file structure
that's easy to navigate
Functionality Based
on Directory
Auto imported components,
file-based routing, etc


V3 Enhancments
Nuxt 3 adds conventions
and added functionality
v3


routes created based on structure (including dynamic routes)
/pages
/pages/edit-[id].vue
v2
/pages/_id.vue
Dynamic Params
/pages/[id].vue
v3
Dynamic Params
/pages/_.vue
Catch All
/pages/[...slug].vue
Catch All
<NuxtLink to="/123">Post 123</NuxtLink>
routes created based on structure (including dynamic routes)
/pages
v3
Page Meta
// MyPage.vue
definePageMeta({
middleware: ["auth"],
pageTransition: 'fade',
layout: 'blog',
})
useHead({
title: "Hello World"
})v2
Page Meta
// MyPage.vue
export default {
middleware: 'auth',
transition: 'fade',
layout: 'blog',
head() {
return {
title: 'Hello World',
}
}
}

routes created based on structure (including dynamic routes)
/pages
v3
Get Current Route
// MyPage.vue
console.log(useRoute());
v2
Get Current Route
// MyPage.vue
export default {
created(){
console.log(this.$route)
}
}

predictable location to store Vue Single File components
/components
v3
Auto Imports
// it's automatic!v2
Auto Imports
// nuxt.config.js
export default {
components: true
}
🔥 so are composables and utils!
/composables
/utils

predictable location to store Vue Single File components
/components
v3
Client Only
// MyPage.vue
<template>
<ClientOnly>
<MyComponent/>
</ClientOnly>
</template>
v2
Client Only
// MyPage.vue
<template>
<ClientOnly>
<MyComponent/>
</ClientOnly>
</template>

predictable location to store Vue Single File components
/components
v2
Client Only
// MyPage.vue
<template>
<ClientOnly>
<MyComponent/>
</ClientOnly>
</template>
v3
Client Only
// MyPage.vue
<template>
<MyComponent/>
</template>
MyComponent.client.vue
MyComponent.server.vue

predictable location to store Vue Single File components
/components
MyComponent.client.vue
v2
Client Only
// MyPage.vue
<template>
<ClientOnly>
<MyComponent/>
</ClientOnly>
</template>
v3
Client Only
// MyPage.vue
<template>
<MyComponent/>
</template>
// MyComponent.server.vue
<template>
Loading...
</template>
MyComponent.server.vue
MyComponent.client.vue

predictable location to store Vue Single File components
/components
MyComponent.client.vue
v2
Client Only
// MyPage.vue
<template>
<ClientOnly>
<MyComponent/>
</ClientOnly>
</template>
v3
Client Only
// MyPage.vue
<template>
<MyComponent/>
</template>
// MyComponent.client.vue
<script setup>
$fetch("http://myapi.com")
</script>
MyComponent.client.vue

lazy load components by prefixing with "lazy"
/components
<LazyMountainsList v-if="show" />- useful if component is not always needed
- delay loading component until the right moment
- optimize bundle size

combine directory structure to assemble component name
/components
(Duplicate segments are removed)

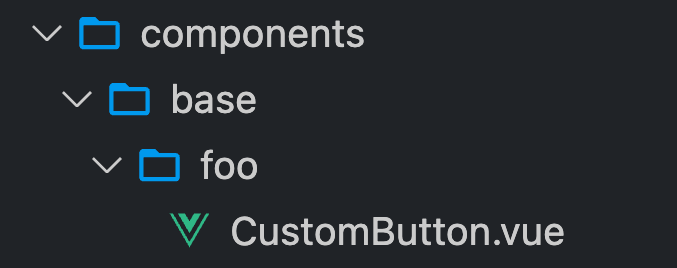
<BaseFooCustomButton />
extract common UI or code patterns into reusable layouts
/layouts
v3
Render Page
// layouts/default.vue
<template>
<div>
<slot />
</div>
</template>
v2
Render Page
// layouts/default.vue
<template>
<Nuxt />
</template>
⚠️ must provide wrapper!

extract common UI or code patterns into reusable layouts
/layouts
v3
Render Page
// ~/error.vue
<template>
<pre> {{error}} </pre>
</template>
<script setup>
defineProps({
error: Object
})
</script>
v2
Error Page
// layouts/error.vue
<template>
<pre> {{error}} </pre>
</template>
<script>
export default {
props: ['error'],
}
</script>

run code before navigating to a route
/middleware
- anonymous middleware
- named middleware
- global middleware

run code before navigating to a route
/middleware
v2
Global Middleware
// nuxt.config.js
export default{
router: {
middleware: 'log',
},
}
~/middleware/log.js
v3
Global Middleware
~/middleware/log.global.js

run code before navigating to a route
/middleware
v2
Middleware Definition
// middleware/log.js
export default function (context) {
console.log("hello")
}
v3
Middleware Definition
// middleware/log.js
export default defineNuxtRouteMiddleware((to, from) => {
console.log("hello")
})
run code before navigating to a route
/middleware
v2
Middleware Definition
// middleware/log.js
export default function ({redirect}) {
return redirect("/login")
}v3
Middleware Definition
// middleware/log.js
export default defineNuxtRouteMiddleware((to, from) => {
return navigateTo('/login')
})
provide global helpers, register Vue plugins and directives
/plugins
v2
Register Plugins
// nuxt.config.js
export default {
plugins: ['~/plugins/tooltip.js']
}
v3
Register Plugins
🔥 auto registered!

provide global helpers, register Vue plugins and directives
/plugins
v2
Register Vue Plugin
// ~/plugins/tooltip.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import VTooltip from 'v-tooltip'
Vue.use(VTooltip)v3
Register Vue Plugin
// ~/plugins/tooltip.js
import VTooltip from 'v-tooltip'
export default defineNuxtPlugin((nuxtApp) => {
nuxtApp.vueApp.use(VTooltip)
})

provide global helpers, register Vue plugins and directives
/plugins
v2
Register Vue Plugin
// ~/plugins/tooltip.client.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import VTooltip from 'v-tooltip'
Vue.use(VTooltip)v3
Register Vue Plugin
// ~/plugins/tooltip.client.js
import VTooltip from 'v-tooltip'
export default defineNuxtPlugin((nuxtApp) => {
nuxtApp.vueApp.use(VTooltip)
})

provide global helpers, register Vue plugins and directives
/plugins
v2
Global Helpers
// ~/plugins/tooltip.js
export default ({ app }, inject) => {
inject(
'hello',
msg => console.log(`Hello ${msg}!`)
)
}v3
Global Helpers
// ~/plugins/tooltip.js
export default defineNuxtPlugin(() => {
return {
provide: {
hello: (msg: string) => `Hello ${msg}!`
}
}
})
provide global helpers, register Vue plugins and directives
/plugins
v2
Global Helpers
// MyComponent.vue
<template>
<div>{{ $hello('world') }}</div>
</template>v3
Global Helpers
// MyComponent.vue
<template>
<div>{{ $hello('world') }}</div>
</template>
provide global helpers, register Vue plugins and directives
/plugins
v2
Global Helpers
// MyComponent.vue
<script>
export default {
created() {
this.$hello('mounted')
}
}
</script>v3
Global Helpers
// MyComponent.vue
<script setup lang="ts">
const { $hello } = useNuxtApp()
</script>
Just use a composable 🤔

Other miscellaneous changes made to the file structure
File Structure Misc.
v2
Static Assets

v3
Static Assets


Other miscellaneous changes made to the file structure
File Structure Misc.
v2
State Management

(Talk more about this later)

Other miscellaneous changes made to the file structure
File Structure Misc.
v2
Server Directory
🤷
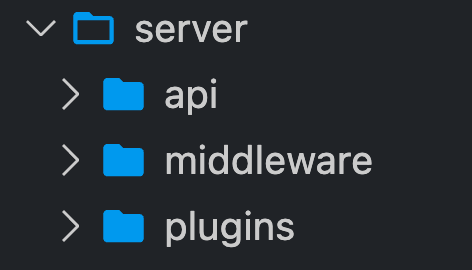
v3
Server Directory
REST api routes
runs on every request (including api)
nitro plugins
(Talk more about this later)

Other miscellaneous changes made to the file structure
File Structure Misc.
v2
app.vue
🤷
v3
app.vue
// app.vue
<template>
<NuxtLoadingIndicator />
// Can add your own app-wide custom stuff
<AppHeader/>
<NuxtLayout>
<NuxtPage/>
</NuxtLayout>
</template>
<style>
// good place to register global CSS
@import "@/assets/main.css";
</style>
Questions?
🙋
Exercise
2
Lunch Break
🍔
40 mins
Data Fetching and Server API Routes
3
Data Fetching
<script>
export default {
async asyncData({ params, $http }) {
const post = await $http.$get(`...`)
return { post }
}
}
</script>v2
Page Level Data Fetching
(blocks route navigation)
Data Fetching
<script>
export default {
async fetch() {
this.posts = await this.$http.$get('...')
},
}
</script>v2
Component Level Data Fetching
provides shortcuts for rendering loading states
Data Fetching
v3
useAsyncData
useFetch
&
useAsyncData
- works in pages, components, and plugins
- used to fetch data that resolves async
useAsyncData
<script setup>
const { data } = await useAsyncData(() => $fetch('/api/count'))
</script>
<template>
Page visits: {{ data }}
</template>
Can be anything that resolves async
Must await (works with suspense)
data is return of callback
smart built-in for http requests
useAsyncData
<script setup>
const { data } = await useAsyncData('unique_key', () => $fetch('/api/count'))
</script>
<template>
Page visits: {{ data }}
</template>
Can also take a unique key as first param
(if not provided it's generated based on file name and line number
Key is for caching
useAsyncData
<script setup>
const { data } = await useAsyncData('unique_key', () => $fetch('/api/count'))
</script>
<template>
Page visits: {{ data }}
</template>
Key is for caching
👀 more on this in a later section!
return from useAsyncData
const { data, pending, refresh, error } = await useAsyncData(...)a boolean indicating whether the data is still being fetched
a function that can be used to refresh the data
an error object if the data fetching failed
useAsyncData options
await useAsyncData(()=>{...}, {
// lazy = don't block navigation
lazy: false,
// set default value before function resolves
default: ()=>{},
// fetch the data SSR?
server: true,
// alter the return from function
transform: ()=> {},
// limit data in payload for performance
pick: [],
//watch reactive sources to auto-refresh
watch: [],
// false means only run handler on change of a watcher
immediate: true
})useFetch
<script setup>
const { data } = await useAsyncData(() => $fetch('/api/count'))
</script>
<template>
Page visits: {{ data }}
</template>
Calling fetch in useAsyncData is very common
useFetch
<script setup>
const { data } = await useFetch('/api/count')
</script>
<template>
Page visits: {{ data }}
</template>
useFetch is a shorthand
useFetch
<script setup>
const { data, refresh, error, pending } = await useFetch('/api/count')
</script>
<template>
Page visits: {{ data }}
</template>
exposes the same data and functions
useFetch
<script setup>
const { data } = await useFetch('/api/count', {
// all the options that useAsyncData takes plus...
// set the request method
method: "GET",
// set request body
body: { foo: "bar" },
// set request headers
headers: [{ Authorization "Bearer 1232342" }],
// set baseURL
baseURL: "https://mysite.com"
})
</script>
<template>
Page visits: {{ data }}
</template>
takes useAsyncDataOptions plus more
useFetch
<script setup>
const skip = ref(0);
const url = computed(()=> `/api/count?skip=${skip.value}`)
const { data } = await useFetch(url)
</script>
<template>
Page visits: {{ data }}
</template>
use reactive url to automatically resend the request whenever URL changes

useFetch
<script setup>
const skip = ref(0);
const { data } = await useFetch(()=> `/api/count?skip=${skip.value}`)
</script>
<template>
Page visits: {{ data }}
</template>
or provide a callback function

Both Come in
Lazy
Versions
useLazyAsyncData
useLazyFetch
&
useLazyAsyncData
useLazyFetch
- does not block navigation
- can show loading indicator on page where data is fetched
- still renders server side on direct page visit
- must handle null data or check pending
useLazyAsyncData
useLazyFetch
<script setup>
const { data, pending } = await useLazyFetch("...");
</script>
<template>
<!-- or could be v-if="!data" -->
<div v-if="pending">loading</div>
<div v-else>
{{ data }}
</div>
</template>Where do I fetch data from?
- Can be an external API (like https://dummyjson.com)
- Server API Routes
Server API Routes
Create a new Server API Route
npx nuxi add api HelloWorldServer API Routes
Produces this file in /server/api/HelloWorld.ts
export default defineEventHandler((event) => {
return 'Hello HelloWorld'
})Server API Routes
Function that returns the response body
export default defineEventHandler((event) => {
return 'Hello HelloWorld'
})Return a string
Server API Routes
Function that returns the response body
export default defineEventHandler(async (event) => {
// make requests to third-party services, APIs
// talk to your database
// etc
return 'Hello HelloWorld'
})Can return a promise to perform async operations
Server API Routes
Function that returns the response body
export default defineEventHandler((event) => {
return {
"foo": "bar",
"activated": true,
"nested":{
"you": "bet"
}
}
})Or JavaScript data that is serializable to JSON
Server API Routes
Use util functions from h3 to get request info
export default defineEventHandler((event) => {
const body = readBody(event);
const myCookie = getCookie(event, "myCookie");
const queryString = getQuery(event);
// etc
return {...}
})Will always pass the event
Server API Routes
Then consume with useFetch
const { data } = await useFetch('/api/HelloWorld')Server API Routes
Route shows up in autocomplete options thanks to TS
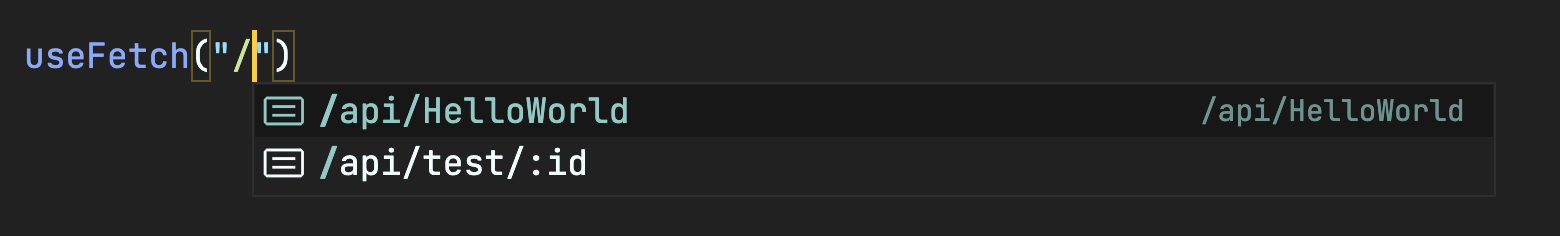
Server API Routes
Plus the data is automatically typed based on the return from the API route
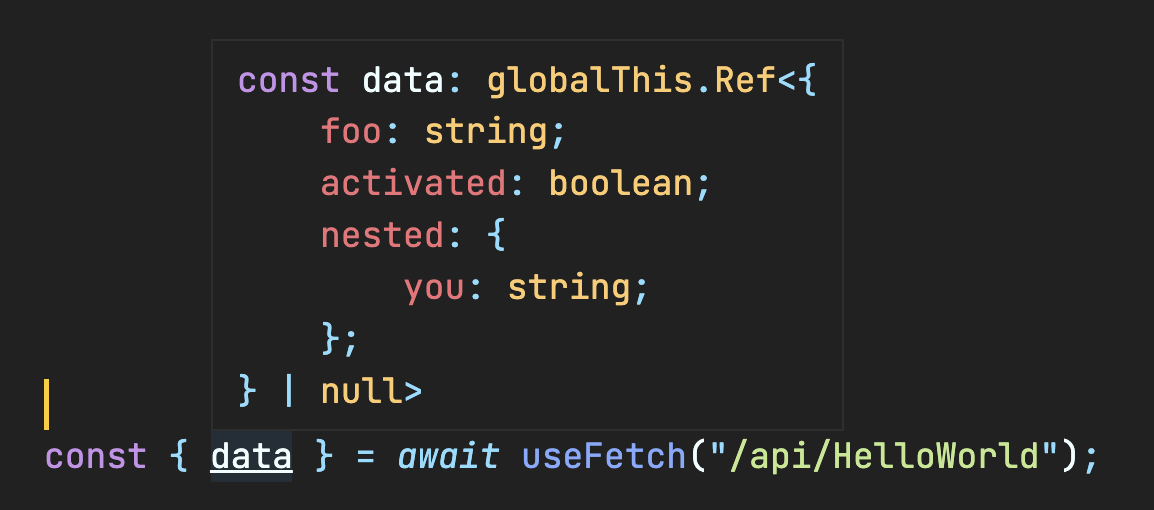
Server API Routes
Like pages you can use dynamic params
/server/api/posts/[id].tsgetRouterParams(event)
Server API Routes
Specify handler by request method
/server/api/posts/[id].get.ts
/server/api/posts/[id].post.ts
/server/api/posts/[id].put.ts
/server/api/posts/[id].delete.tsQuestions?
🙋
Exercise
3
Coffee Break
☕️
15 mins
Nuxt Devtools
4
End of Day everyone is getting a little tired
Saved devtools for last because it will
rev you up!

Nuxt Devtools

Nuxt Devtools
npx nuxi devtools enable
Nuxt Devtools
Open devtoosl here

Nuxt Devtools

Welcome message on first install

Nuxt Devtools
Overview of project


Nuxt Devtools
List of all routes
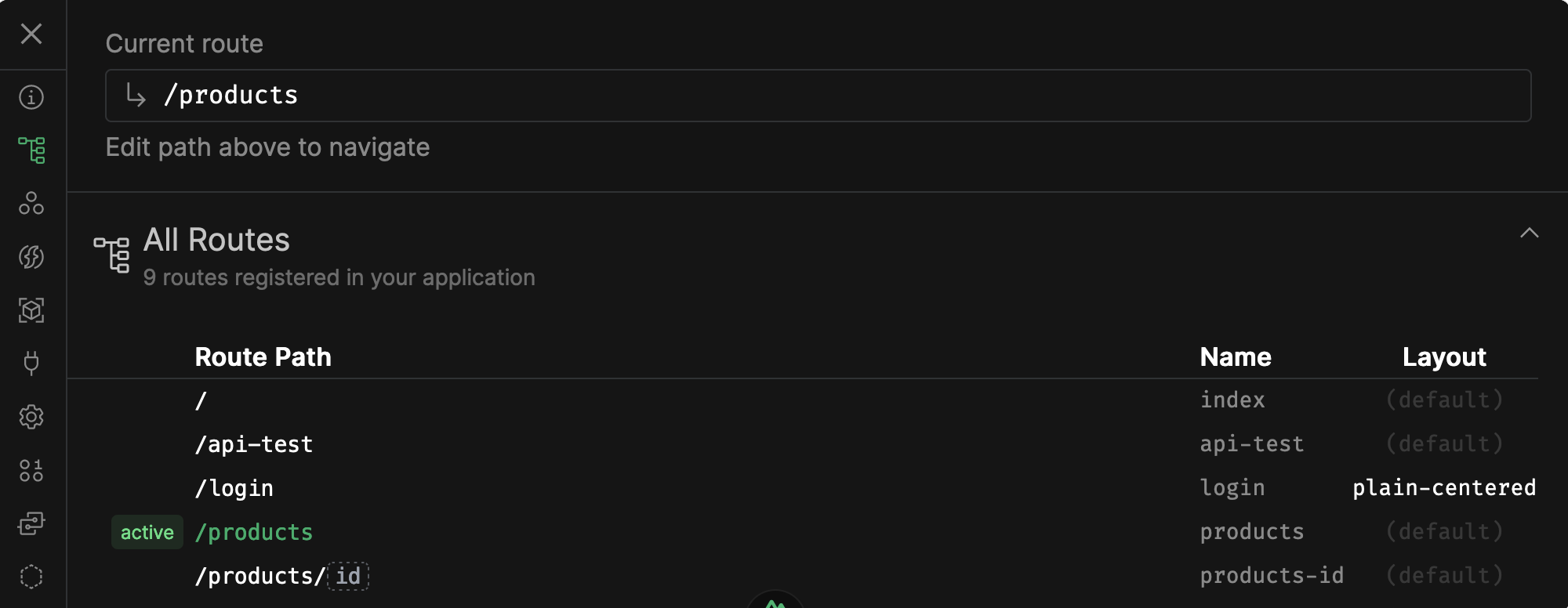
- Click to visit route
- and can also open file in IDE

Nuxt Devtools
List all Components
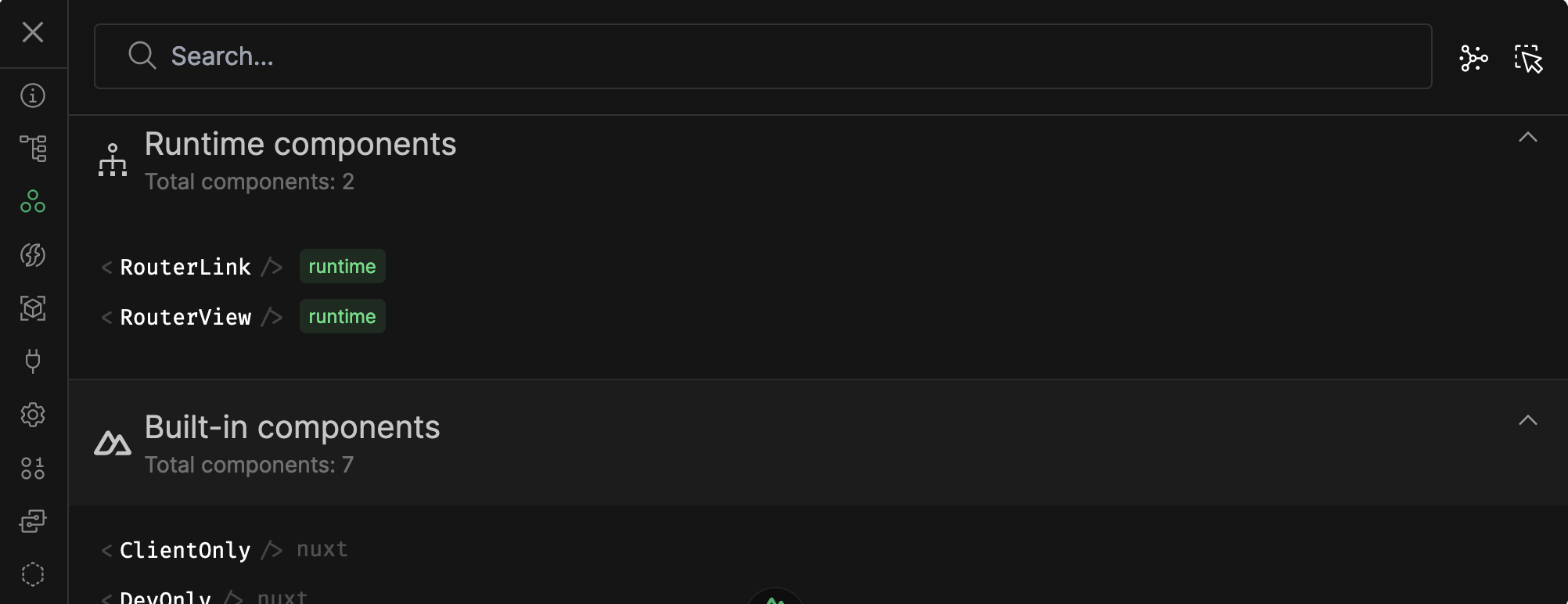

Nuxt Devtools
List all Components
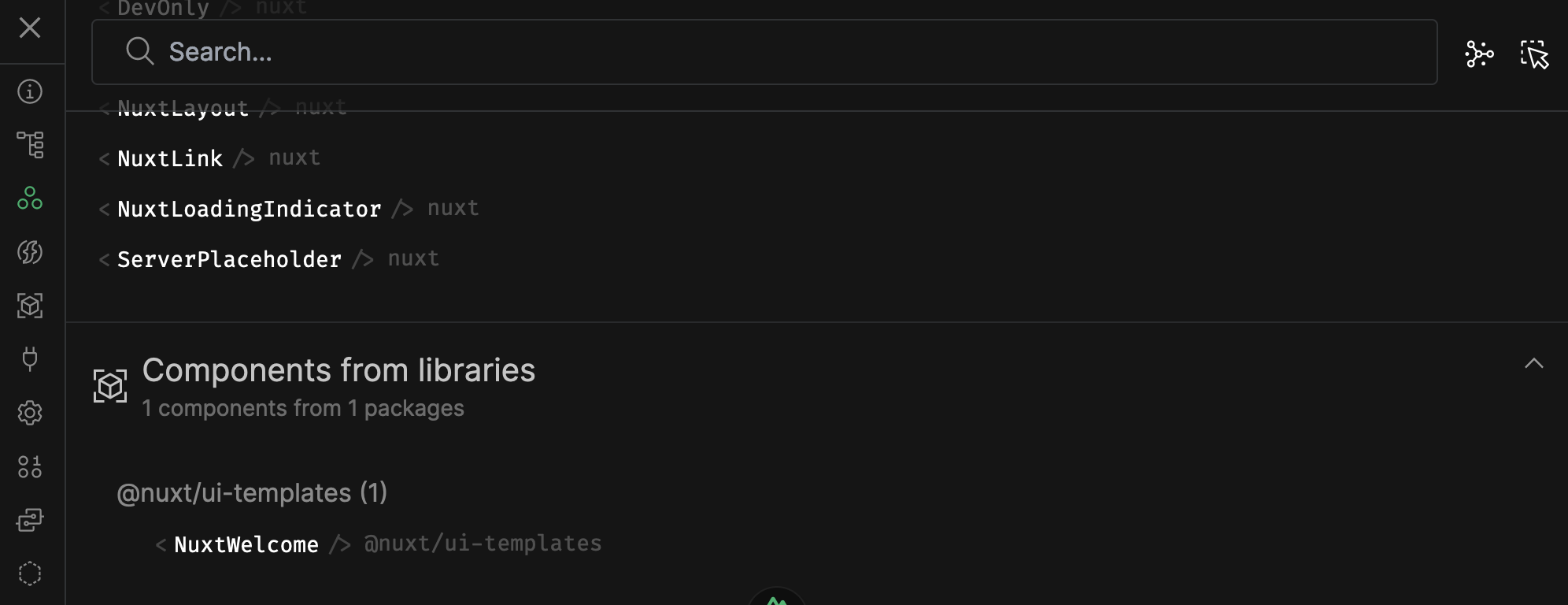

Nuxt Devtools
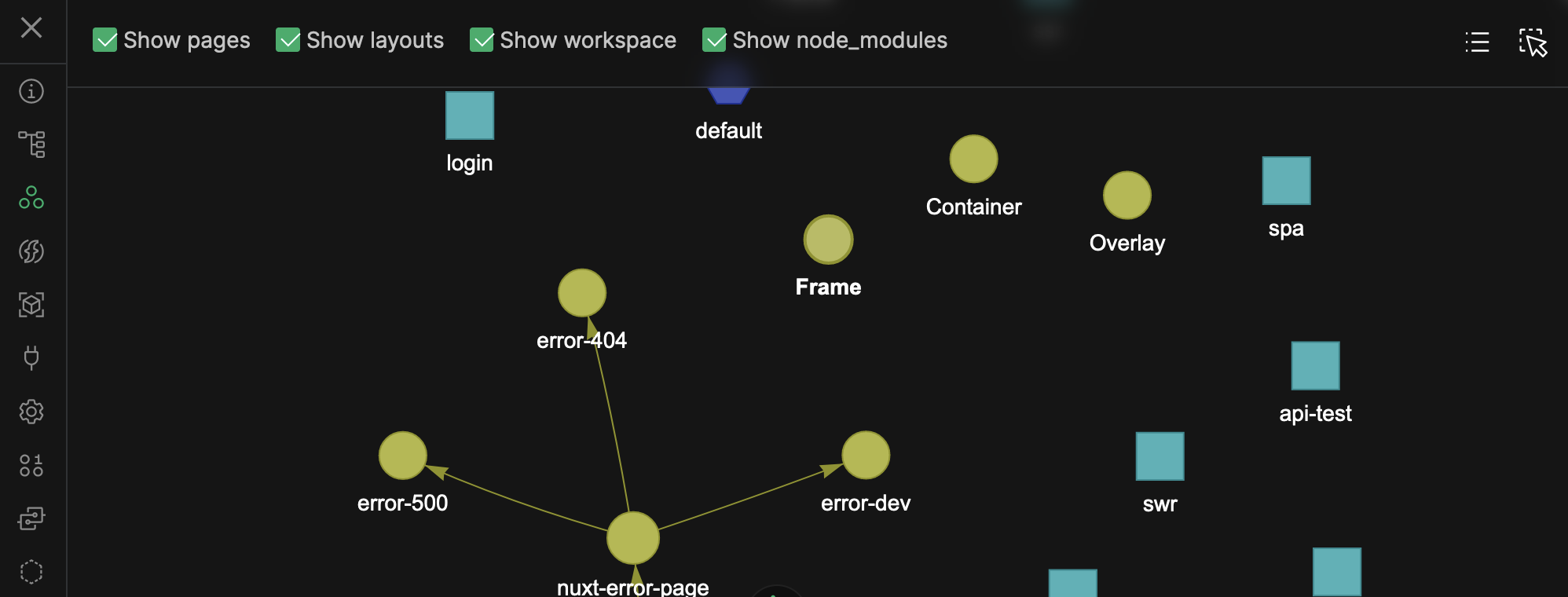
Components Graph to Visualize Deps and Types

Nuxt Devtools
Inspect components on page
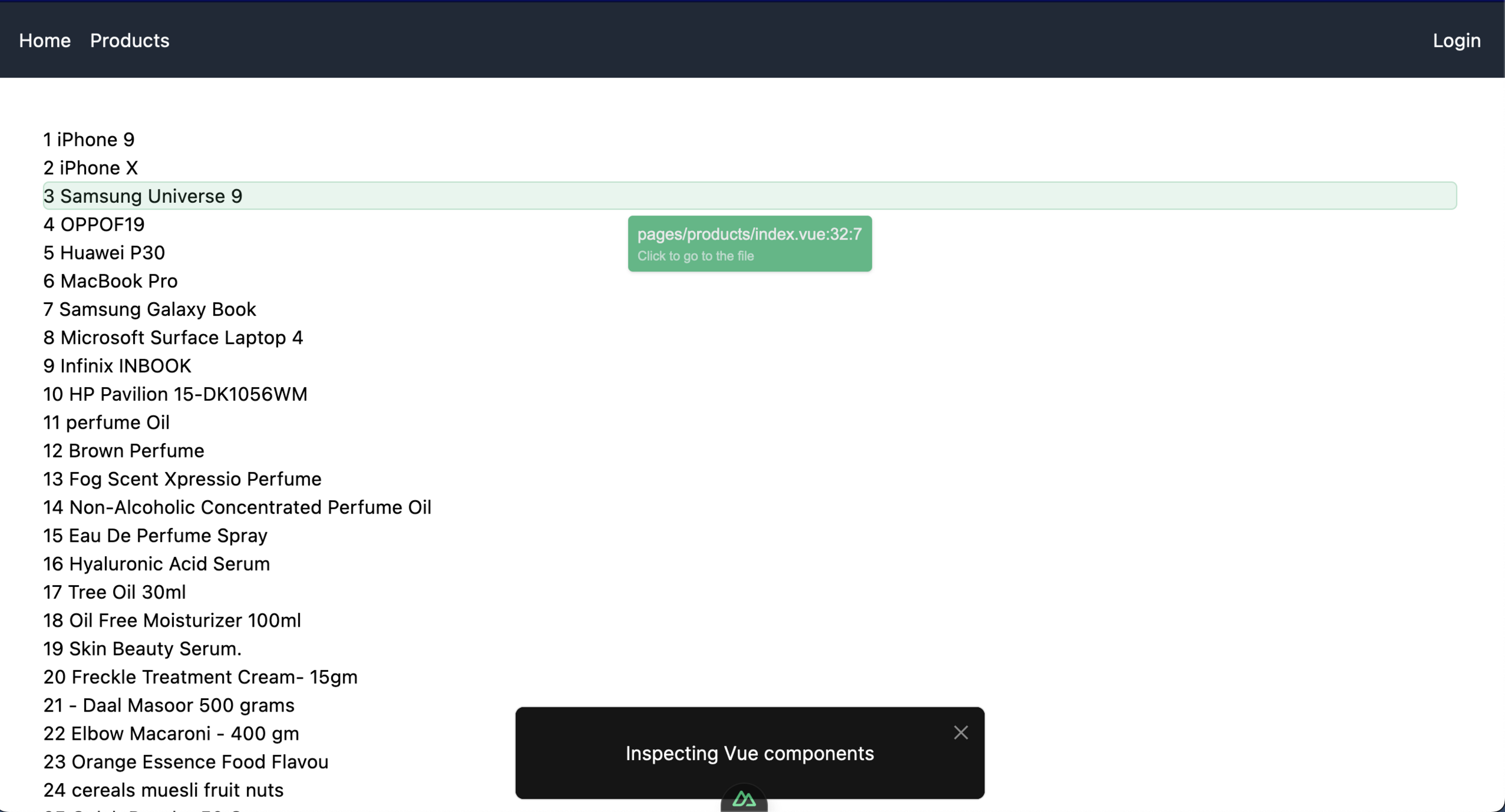

Nuxt Devtools
View built in composables and those from libraries
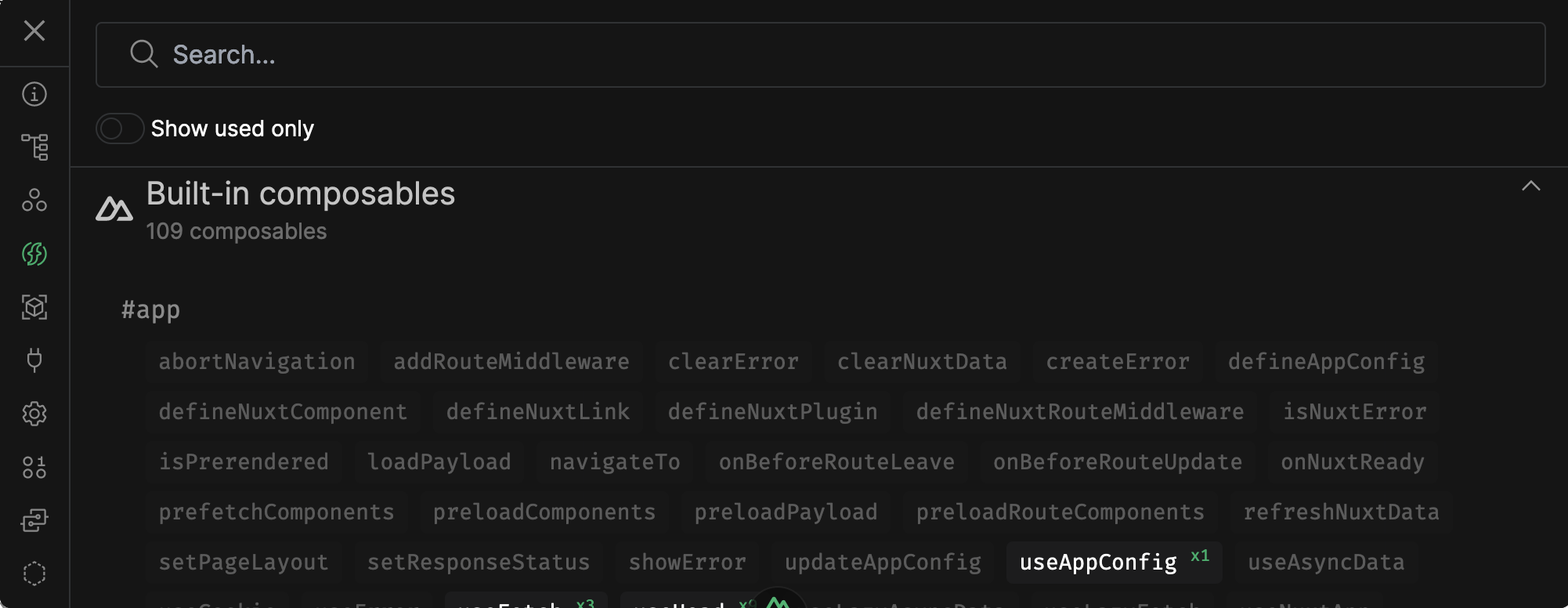
Grayed out are available but not used
Solid white are used

Nuxt Devtools
View installed modules
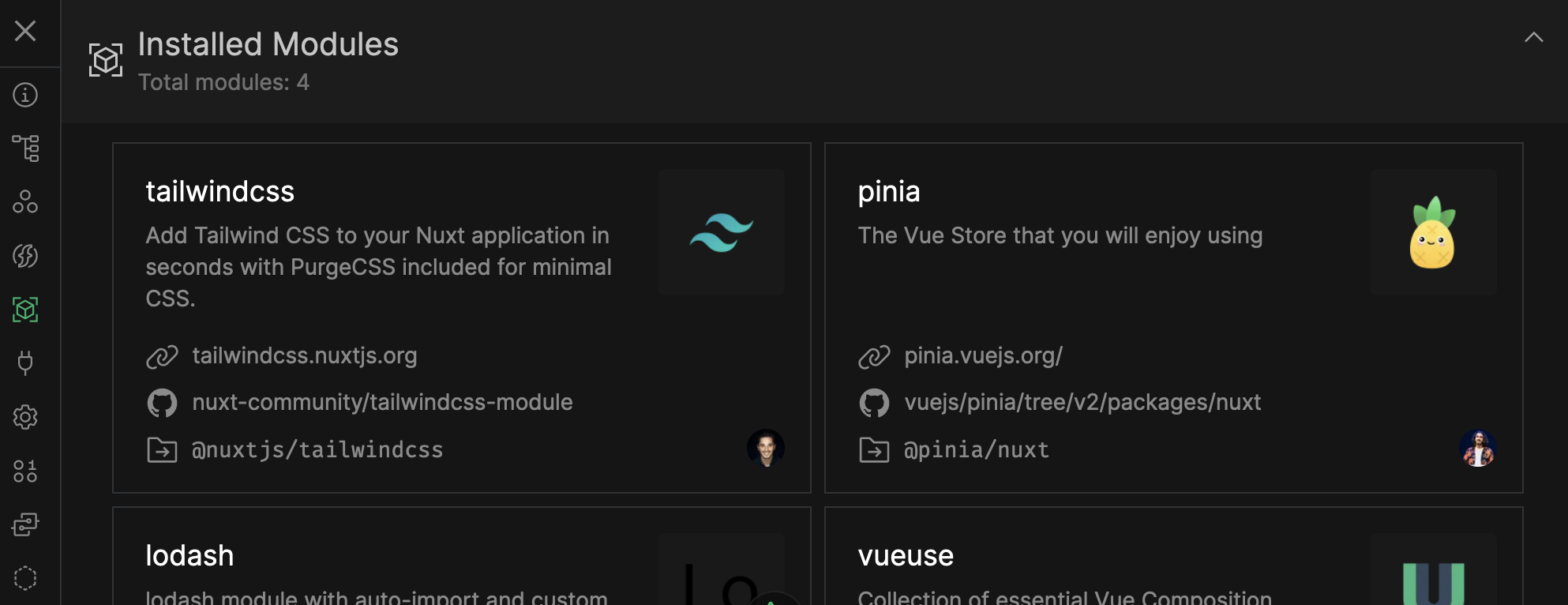
Docs
Github
File System

Nuxt Devtools
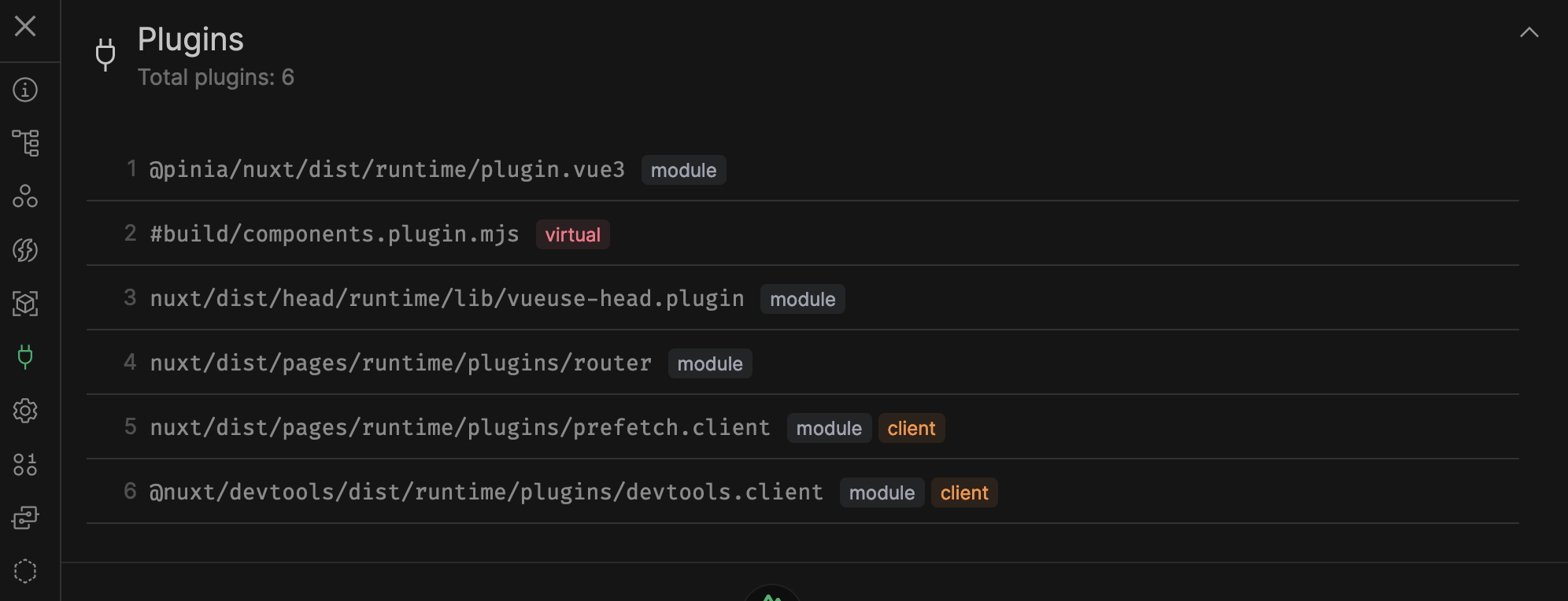
Installed plugins and where they're from

Nuxt Devtools
Runtime and App Configs
We'll talk more about these later

Nuxt Devtools
State created with useState and fetched with useFetch/useAsyncData
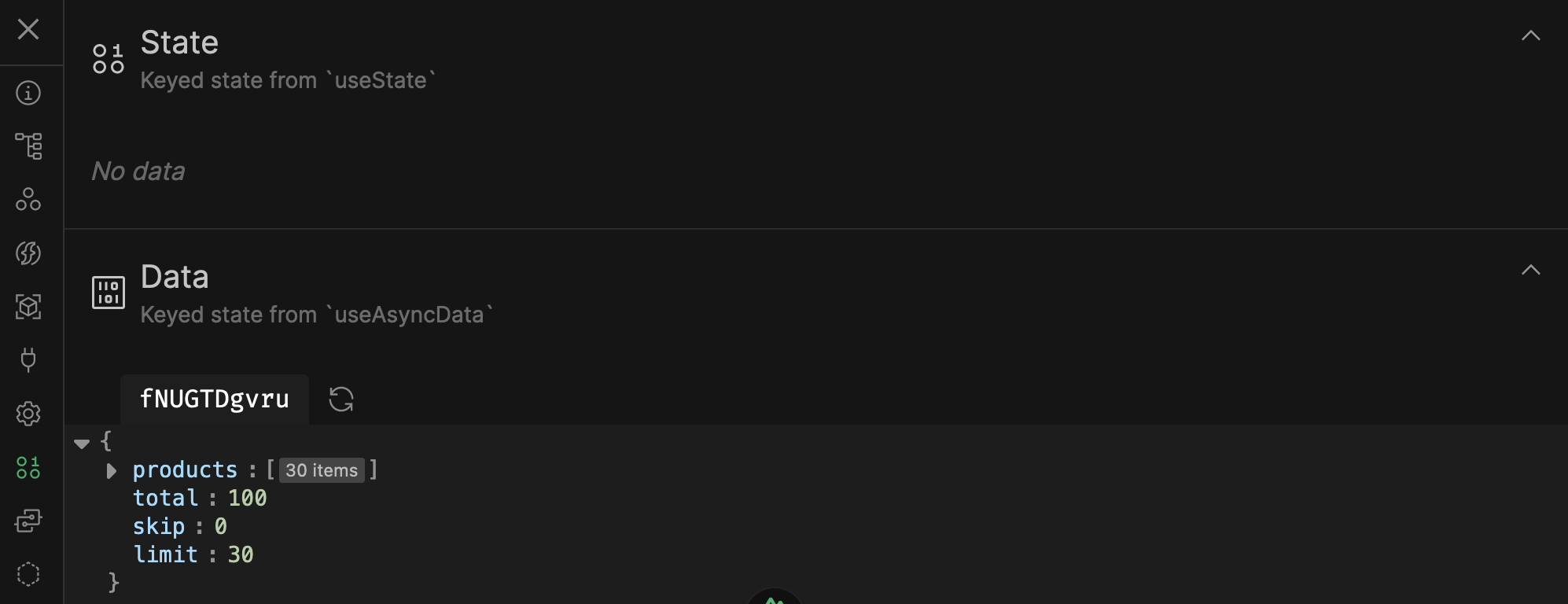
(More on using this cache and state later)
It's cached under this key
The data we fetched in the exercise

Nuxt Devtools
Monitor the time spent in each hook
Help debug performance issues
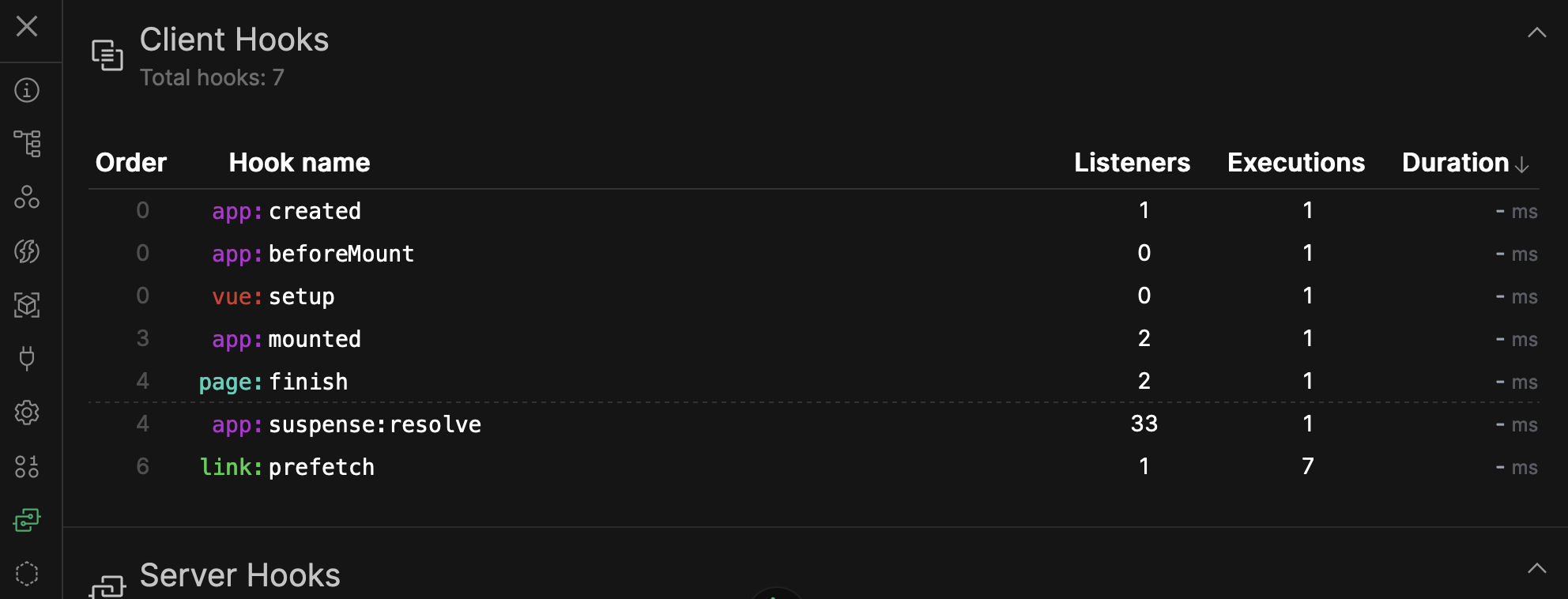

Nuxt Devtools
Monitor the time spent in each hook
Help debug performance issues
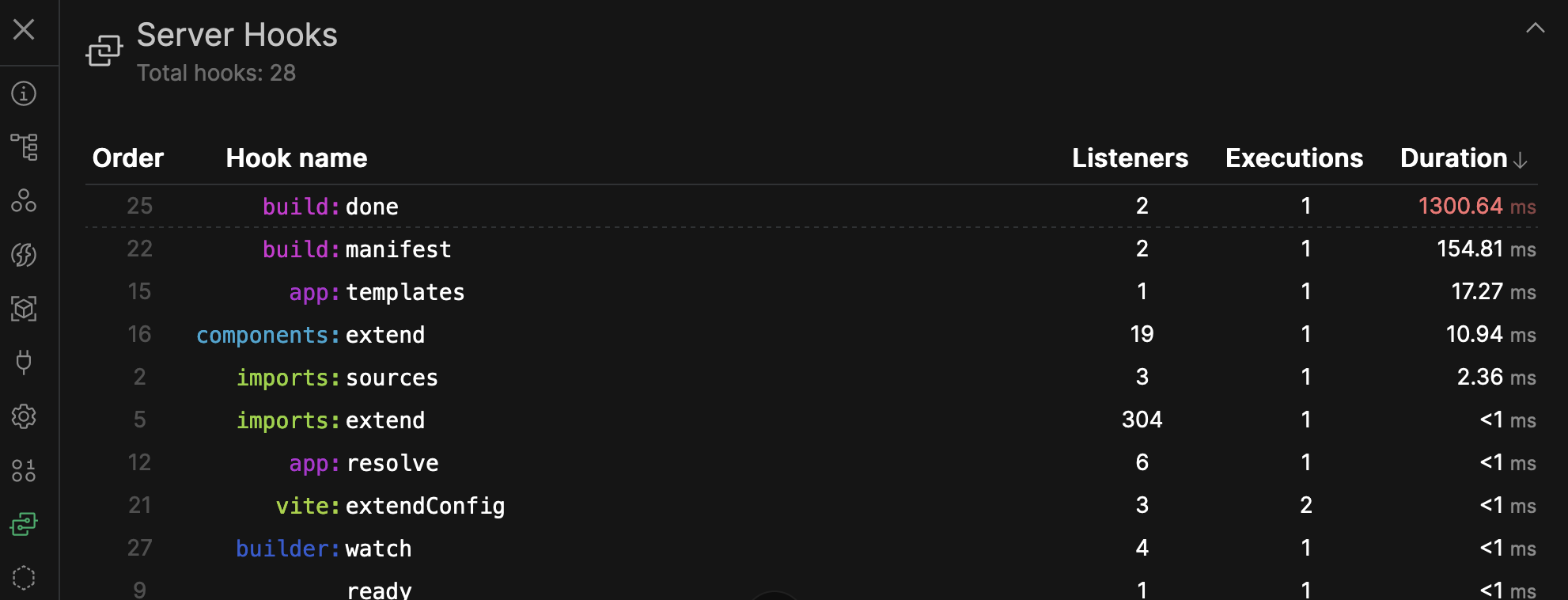

Nuxt Devtools
Virtual files generated by Nuxt to support conventions
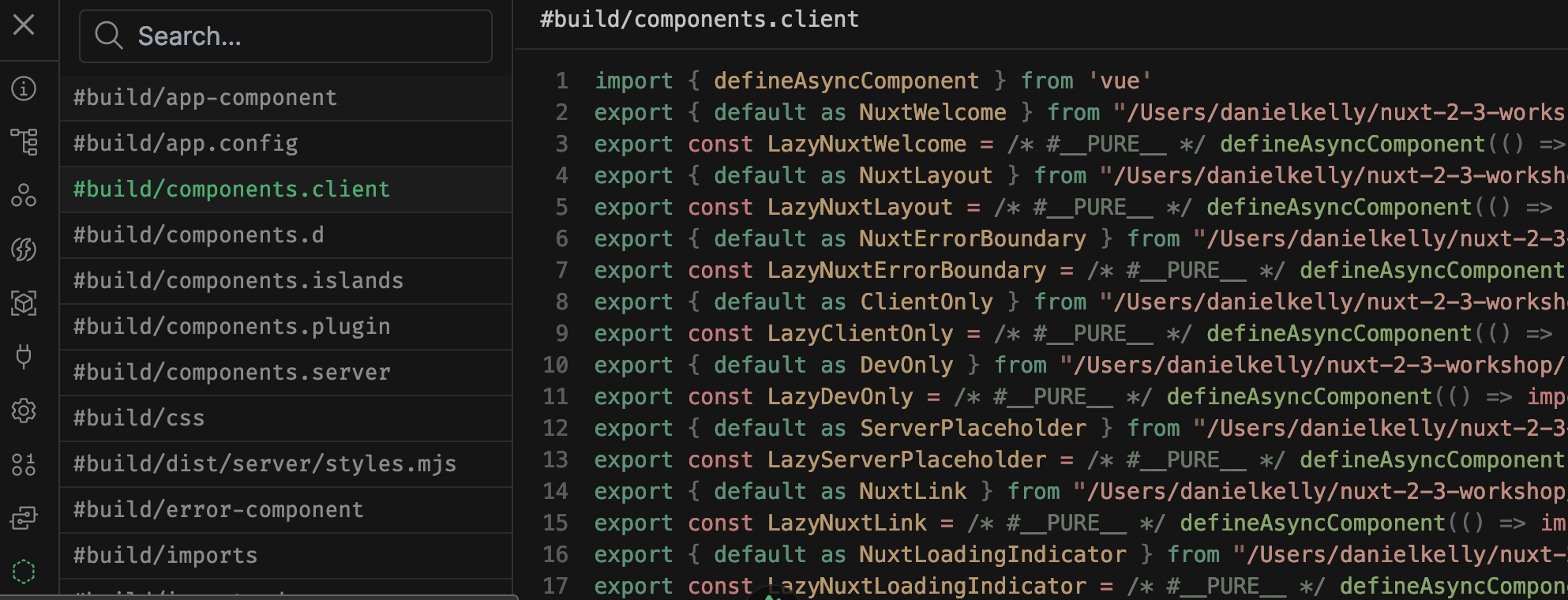

Nuxt Devtools
Inspect transformation steps of Vite
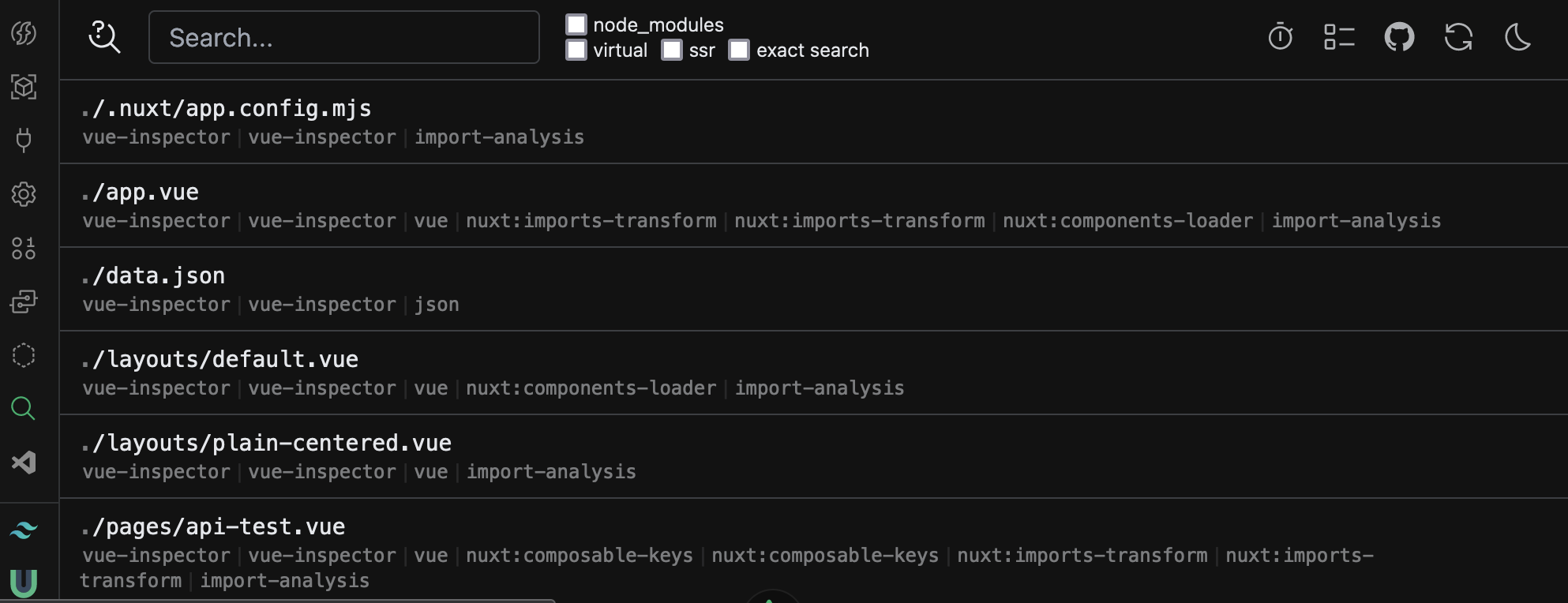

Nuxt Devtools
Inspect transformation steps of Vite
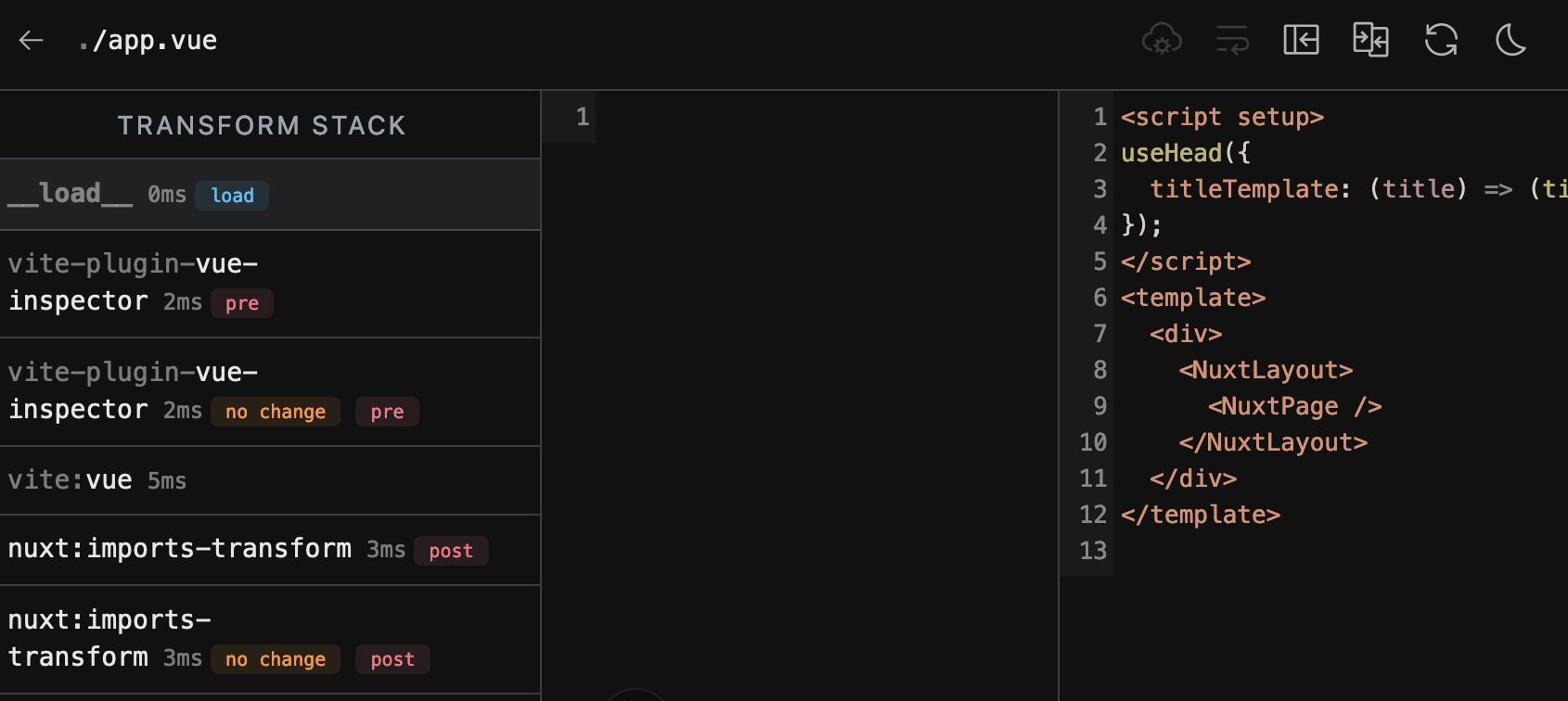



Nuxt Devtools
Modules can install their own extensions


Nuxt Devtools
Modules can install their own extensions
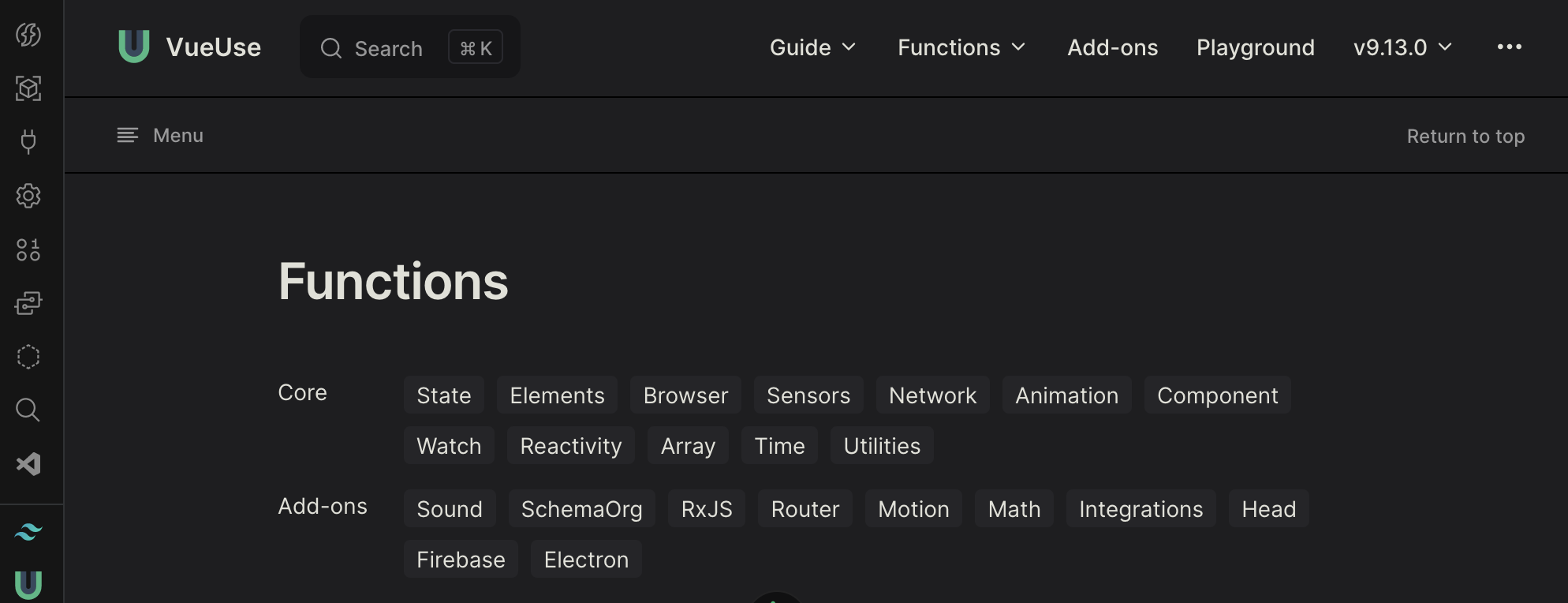
Questions?
🙋
Exercise
4
Q&A
❓
Day 2
👋
Welcome Back!
Global State Management
5

Global State Management
Why?
- Share state across components
- Avoid prop drilling
- Even share state across pages (usually for performance)

Global State Management
How?

In Nuxt 2, the answer was Vuex

Global State Management
What about in
Nuxt 3?
🙋
💬
Answers in the Chat, please

Global State Management

Pinia
Many people say
✅

Global State Management
Several Options
- Pinia
- useState (built in composable)
- useNuxtData (kinda) (built in composable)
- Vuex (good if migrating)
Pinia

- Devtools support
- A timeline to track actions, mutations
- Stores appear in components where they are used
- Time travel and easier debugging
- Hot module replacement
- Modify your stores without reloading your page
- Keep any existing state while developing
Pinia

- Plugins: extend Pinia features with plugins
- Proper TypeScript support or autocompletion for JS users
- Server Side Rendering Support
How does Pinia work?
2 options

Pinia

// stores/counter.js
import { defineStore } from 'pinia'
export const useCounterStore = defineStore('counter', {
state: () => {
return { count: 0 }
},
getters: {
double: (state) => state.count * 2,
},
actions: {
increment() {
this.count++
},
},
})
Option Store
Great if you familiar
with Vuex options
Pinia

// stores/counter.js
export const useCounterStore = defineStore('counter', () => {
const count = ref(0)
const doubled = computed(()=> count.value * 2)
function increment() {
count.value++
}
return { count, increment }
})
Setup Store
Great if you prefer composable style
Pinia

// MyComponent.vue
<script setup>
import { useCounterStore } from '@/stores/counter'
const counter = useCounterStore()
counter.count++
// or using an action instead
counter.increment()
</script>
Accessing the state is easy and TypeSafe
Pinia

// MyComponent.vue
<script setup>
import { useCounterStore } from '@/stores/counter'
const counter = useCounterStore()
counter.count++
// or using an action instead
counter.increment()
</script>
Accessing the state is easy and TypeSafe
Vuex
// plugins/vuex.ts
import { createStore } from "vuex";
import * as rootStore from "@/store/index";
export default defineNuxtPlugin((nuxtApp) => {
const store = createStore(rootStore);
nuxtApp.vueApp.use(store);
});
Only choose to ease migration process


useState()
Built in composable for global state management
- SSR-friendly shared state across components
- preserved after server-side rendering (during hydration)
- shared across all components using a unique key
- only work in setup or lifecycle hooks
(you can use in composable that's called in setup) - must be serializable to JSON

useState()
Anatomy of useState
const count = useState('count', ()=> 0)unique key
(to id this piece of state)
Callback function
returns the initial value
Reactive ref

useState()
Can be defined in component
// CountButton.vue
<script setup>
const count = useState('count', () => 0)
</script>
<template>
<div>
<button @click="count++">
{{ count }}
</button>
</div>
</template>

useState()
And used in another component
// OtherComponent.vue
<script setup>
const count = useState('count', () => 0)
</script>
<template>
<div>
{{ count }}
</div>
</template>
Both instances of count refer to the same state

useState()
Can also use in a composable
// composables/useCount.ts
export function useCount() {
const count = useState("count", () => 0);
return {
count,
};
}
And count will be the same across all components
where the composable is used
const { count } = useCount();
useState()
Similar to this in client-side only environment
// composables/useCount.ts
const count = ref(0);
export function useCount() {
return {
count,
};
}
❌
NOT SSR friendly

useState()
Similar to this in client-side only environment
// composables/useCount.ts
export function useCount() {
const count = useState("count", () => 0);
return {
count,
};
}
So always use useState instead of ref outside of the composable function

useState()
Can also be the composable itself
// composables/useCount.ts
export const useCounter = () => useState('counter', () => 0)// MyComponent.vue
const count = useCount();and use it like so:

useNuxtData()
Retrieve cached data from useAsyncData/useFetch calls
- not strictly a state management solution
- but can replace state management in some cases
- For example, sharing the data of a resource across pages

useNuxtData()
Retrieve cached data from useAsyncData/useFetch calls
/products
List of Products
/products/1
Single Product Page
in the background

useNuxtData()
Retrieve cached data from useAsyncData/useFetch calls
// pages/products/index.vue
const { data, pending } = await useFetch(
() => `https://dummyjson.com/products?skip=${skip.value}&limit=${perPage}`,
{
key: "products",
}
);Specify a key on the fetch
const { data, pending } = await useAsyncData(
"products",
() => ...,
);or provide as first argument to useAsyncData

useNuxtData()
Retrieve cached data from useAsyncData/useFetch calls
// pages/products/[id].vue
const { data: cached } = useNuxtData("products");
const id = computed(() => useRoute().params.id);
const { data: product } = await useLazyFetch(
() => `https://dummyjson.com/products/${id.value}`,
{
key: `product-${id.value}`,
default: () =>
cached.value?.products.find((product) => {
return product.id === Number(id.value);
}),
}
);
useNuxtData()
Can also use useNuxtData for optimistic updates
// pages/todos/index.vue
const { data } = await useFetch('/api/todos', { key: 'todos' })
Imagine we fetched some todos from an API

useNuxtData()
Can also use useNuxtData for optimistic updates
const newTodo = ref('')
const previousTodos = ref([])
// Access to the cached value of useFetch in todos.vue
const { data: todos } = useNuxtData('todos')
const { data } = await useFetch('/api/addTodo', {
key: 'addTodo',
method: 'post',
body: {
todo: newTodo.value
},
onRequest () {
previousTodos.value = todos.value // Store the previously cached value to restore if fetch fails.
todos.value.push(newTodo.value) // Optimistically update the todos.
},
onRequestError () {
todos.value = previousTodos.value // Rollback the data if the request failed.
},
async onResponse () {
await refreshNuxtData('todos') // Invalidate todos in the background if the request succeeded.
}
})
Questions?
🙋
Exercise
5
Coffee Break
☕️
Best Practices
6
Best Practices
What are they and why?
💪
Common patterns to follow for building Nuxt applications
- performance
- code maintainability
- scalability
- often used to describe preference (this is not correct usage)
Best Practices | Performance
Overview
💪
- Nuxt Image - optimize image size/format
- Async components
- Smart 3rd party deps
- Eliminating unneeded reactivity
- Virtual lists
Best Practices | Performance
Nuxt Image
💪
Best Practices | Performance
Nuxt Image
💪
Images are low hanging fruit for performance optimization.
Nuxt Image makes it easy to get a boost!
Best Practices | Performance
Nuxt Image
💪
// image exists at @/public/myImage.jpg
<img src="/myImage.jpg"/>Best Practices | Performance
Nuxt Image
💪
// image exists at @/public/myImage.jpg
<NuxtImg src="/myImage.jpg"/>Best Practices | Performance
Nuxt Image - options for <NuxtImg>
💪
// image exists at @/public/myImage.jpg
<NuxtImg
src="/myImage.jpg"
// actual image is resized before sending to browser (also height)
width="200"
sizes="sm:100vw md:50vw lg:400px"
format="webp"
quality="80"
loading="lazy"
/>Best Practices | Performance
Nuxt Image - options for <NuxtImg>
💪
// image exists at @/public/myImage.jpg
<NuxtImg
src="/myImage.jpg"
// actual image is resized before sending to browser (also height)
width="200"
sizes="sm:100vw md:50vw lg:400px"
quality="80"
loading="lazy"
format="webp"
/>Best Practices | Performance
Nuxt Image - <NuxtPicture>
💪
// image exists at @/public/myImage.jpg
<NuxtPicture src="/myImage.jpg" />Better option is NuxtPicture as it allows the browser to decide the best format
will auto serve webp to browsers that support it and jpg to those that do not
Best Practices | Performance
Nuxt Image - $img utility
💪
const $img = useImage()
const imgUrl = $img(src, modifiers, options)Best Practices | Performance
Even use external images
💪
// nuxt.config.ts
export default defineNuxtConfig({
image: {
domains: ["i.dummyjson.com"],
},
})
<NuxtImg
src="https://i.dummyjson.com/data/products/1/1.jpg"
/>But must add domain to allowlist
Best Practices | Performance
Nuxt Image - FAQ
💪
- Does it work without Cloudinary? Yes (21+ providers)
- Does it work on external images? Yes
- Where do I store local images? /public
Best Practices | Performance
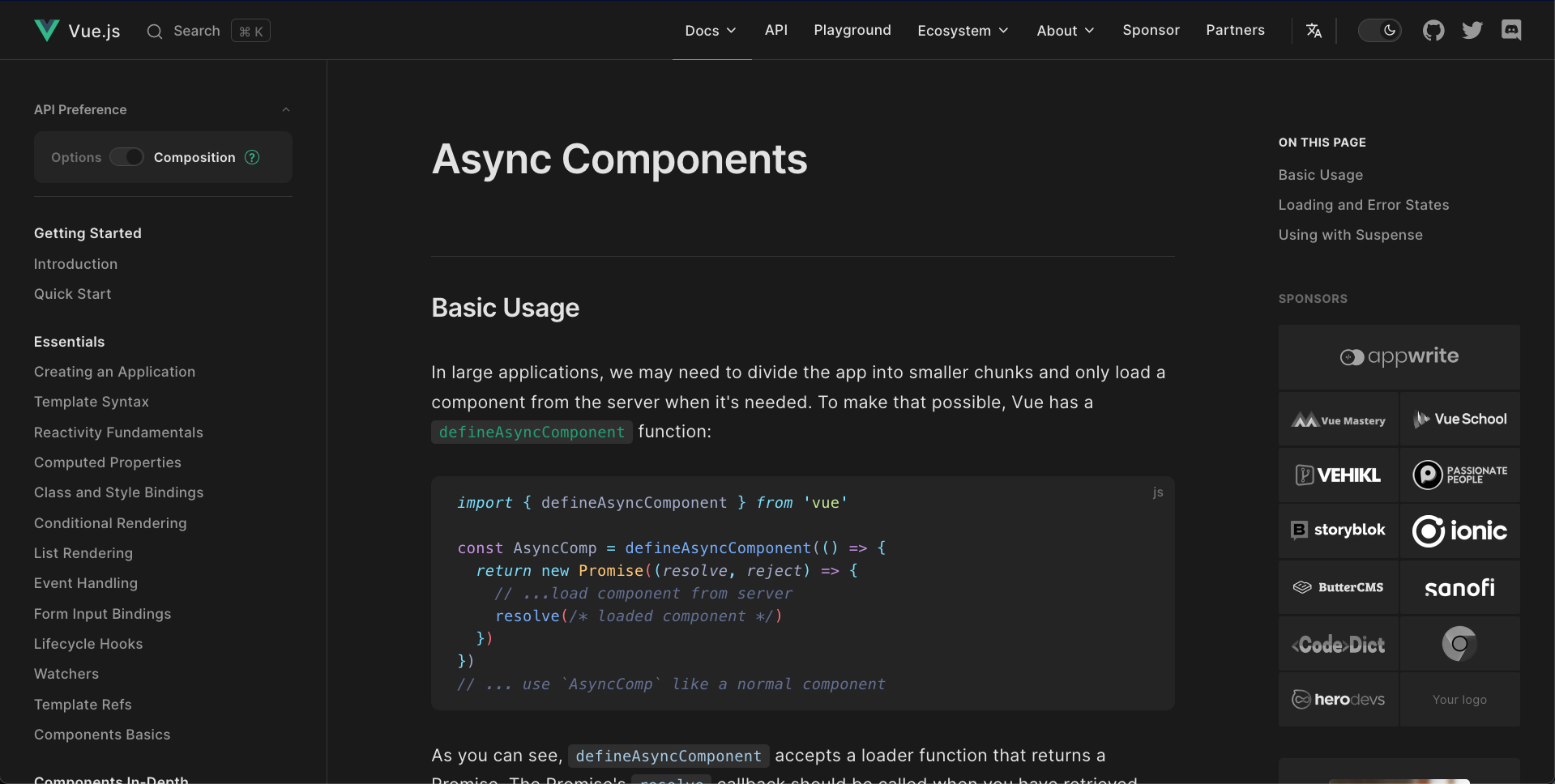
Async components
💪
Best Practices | Performance
Async components
💪
divide the app into smaller chunks and only load a component from the server when it's needed
Best Practices | Performance
Async components
💪
const AsyncComp = defineAsyncComponent(() =>
import('./components/MyComponent.vue')
)Best Practices | Performance
Async components
💪
<script setup>
const AsyncComp = defineAsyncComponent(() =>
import('./components/MyComponent.vue')
)
</script>
<template>
<AsyncComponent v-if="some condition...">
</template> will load a seperate JS file only when condition is true
Best Practices | Performance
Async components
💪
<script setup>
const AsyncComp = defineAsyncComponent(() =>
import('./components/MyComponent.vue')
)
</script>
<template>
<AsyncComponent>
</template> no need to make async if always renders
Best Practices | Performance
Smart 3rd party deps
💪
3rd party deps add hidden weight that often goes uninvestigated
Best Practices | Performance
Smart 3rd party deps
💪
find the cost of adding an npm package to your bundle
Best Practices | Performance
Smart 3rd party deps
💪
Let's take a look at Lodash on bundlephobia
Best Practices | Performance
Smart 3rd party deps
💪
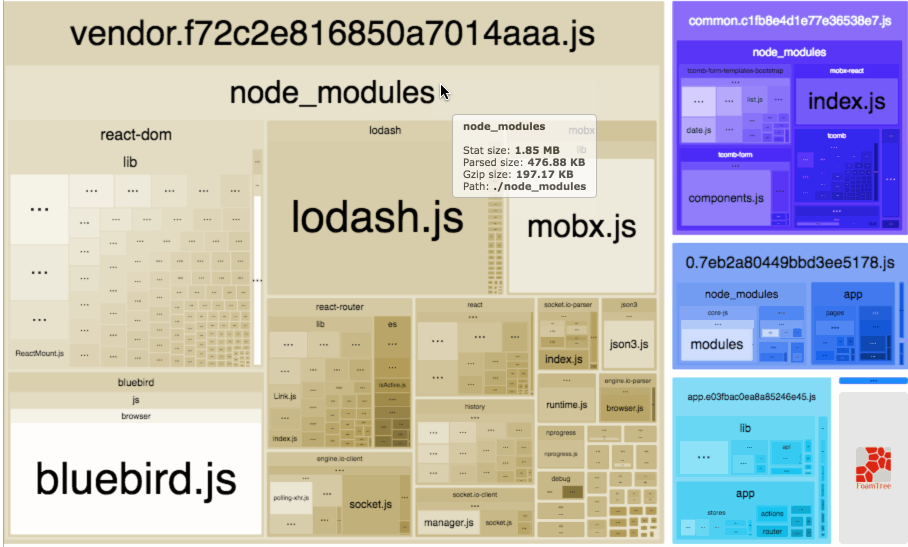
Webpack Bundle Analyzer
Best Practices | Performance
Smart 3rd party deps
💪
Rollup Plugin Visualizer
(for Vite)
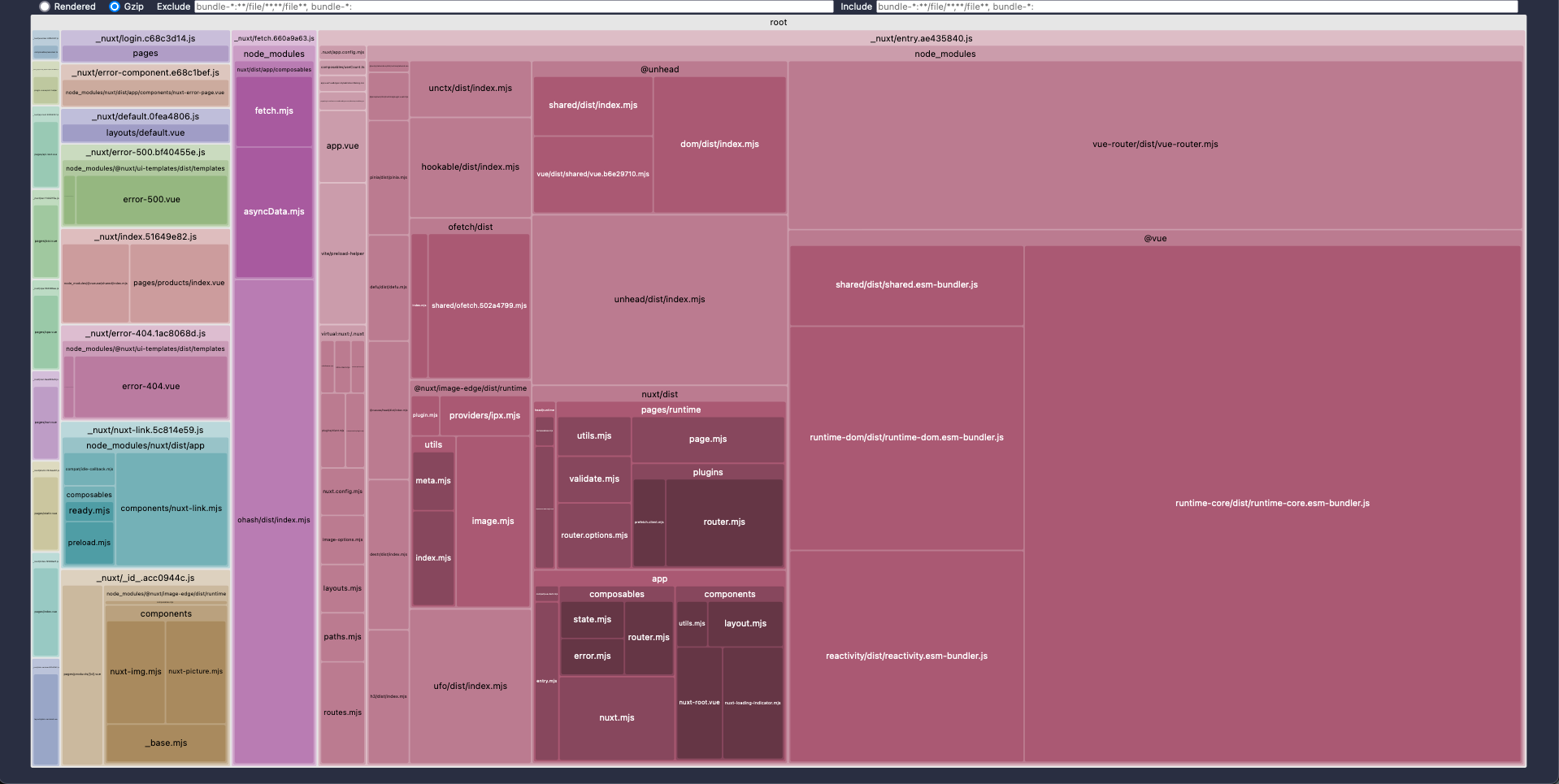
Best Practices | Performance
Smart 3rd party deps
💪
npx nuxi analyzeBest Practices | Performance
Eliminating unneeded reactivity
💪
Sometimes we define variables only for convenience. And they never change, so it's unnecessary for Vue to track it as a dependency
Best Practices | Performance
Eliminating unneeded reactivity
💪
<script setup>
// will never change
const perPage = ref(10);
</script>
<template>
{{ perPage }}
</template>Best Practices | Performance
Eliminating unneeded reactivity
💪
<script setup>
// will never change
const perPage = 10;
</script>
<template>
{{ perPage }}
</template>Best Practices | Performance
Eliminating unneeded reactivity
💪
Some HTML never needs to be hydrated at all
Best Practices | Performance
Eliminating unneeded reactivity
💪
Nuxt Server Components
Best Practices | Performance
Eliminating unneeded reactivity
💪
// Markdown.vue
<script setup lang="ts">
import MarkdownIt from "markdown-it";
const md = new MarkdownIt();
const props = defineProps<{
md: string;
}>();
var result = md.render(props.md);
</script>
<template>
<div v-html="result"></div>
</template>
Example
Markdown
Component
Best Practices | Performance
Eliminating unneeded reactivity
💪
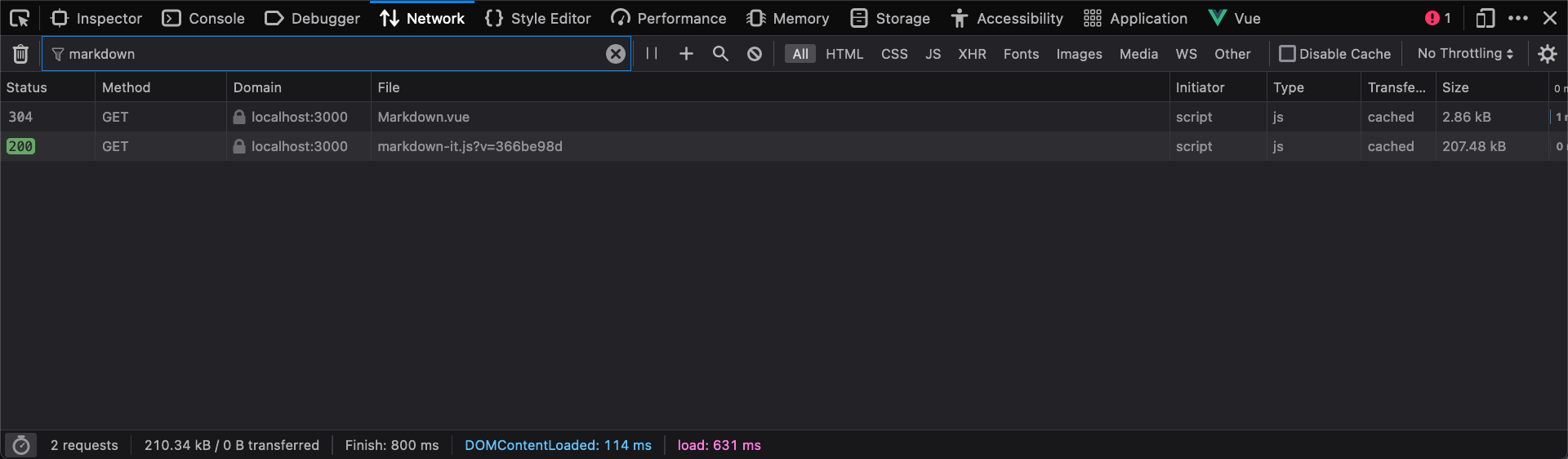
Normally the component js and the markdown-it library are downloaded and run in browser
Best Practices | Performance
Eliminating unneeded reactivity
💪
Markdown.server.vue
append server to the component name to render ONLY on the server side with NO client side JS
Best Practices | Performance
Eliminating unneeded reactivity
💪
- great for content that is mostly static
- if prop value changes ajax request is made for new HTML
- is currently experimental
Best Practices | Performance
Eliminating unneeded reactivity
💪
// nuxt.config.ts
export default defineNuxtConfig({
experimental: {
componentIslands: true,
},
})Best Practices | Performance
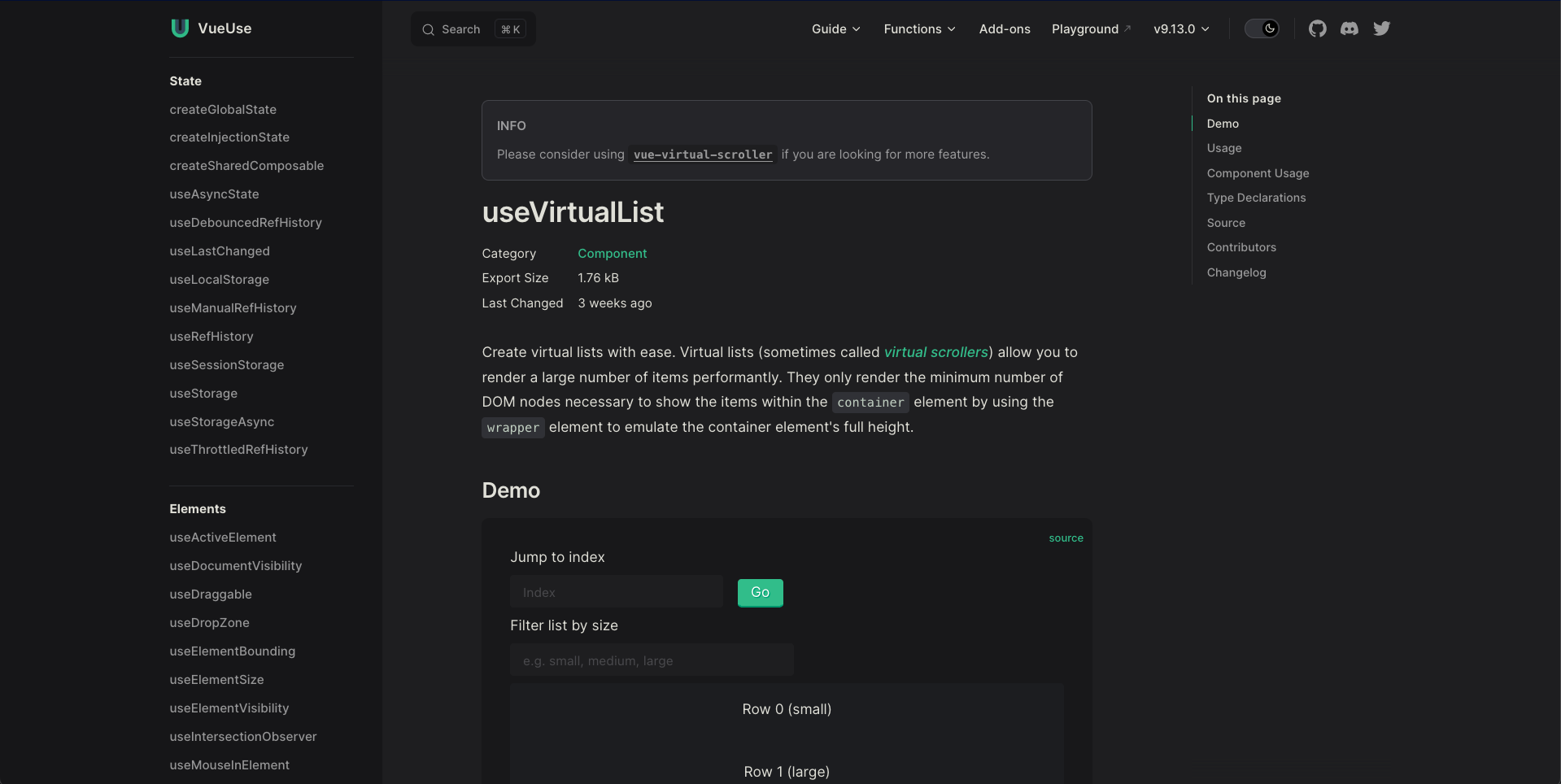
Virtual lists
💪
Sometimes you need to render VERY long lists which can make the page react sluggishly
Best Practices | Performance
Virtual lists
💪
Virutal lists only render the minimum number of DOM nodes necessary to show the items within a container
Best Practices | Performance
Virtual lists
💪
Best Practices | Maintainability/Scalability
Overview
💪
- use TypeScript
- use ESLint
- prefer composables over mixins
- Other tips and tricks
Best Practices | Maintainability/Scalability
TypeScript & ESLint
💪
- helps you catch errors directly in your IDE
- gives your IDE autocomplete super powers
(even on component props and events) - makes refactors less risky and less stressful
Best Practices | Maintainability/Scalability
TypeScript & ESLint
💪
No time to dive into details



Live Talk at Vue.js Amsertdam
Best Practices | Maintainability/Scalability
Composables vs Mixins
💪
- makes sources of data/methods more clear
- prevents naming collisions
- allows for private reactive data
Best Practices | Maintainability/Scalability
Composables vs Mixins
💪
No time to dive into details
Best Practices | Maintainability/Scalability
Other Tips and Tricks
💪
- separate logic from presentation
- use :key on loops
- maintain a predictable naming conventions based on the Vue.js style guide
- minimize direct DOM manipulation
(use template refs otherwise) - validate props with TS or even runtime validations
Questions?
🙋
Exercise
6
Lunch Break
🍔
40 mins
Error Handling
7
Error Handling
- Errors during the Vue rendering lifecycle (SSR + SPA)
- Errors during API or Nitro server lifecycle
- Server and client startup errors (SSR + SPA)
Sources of Errors
Error Handling
How do we handle these errors?
Error Handling
Vue's onErrorCaptured
onErrorCaptured((error, instance, info) => {
// do whatever with the error
});- component level error handling
- catch errors from descendant component
- return false to prevent propagation
Error Handling
Vue's onErrorCaptured
onErrorCaptured((error, instance, info) => {
alert("Sorry, we hit a snag. Please refresh and try again")
});great for performing side affects whenever an error occurs
Error Handling
app level error handling
export default defineNuxtPlugin((nuxtApp) => {
nuxtApp.vueApp.config.errorHandler = (error, context) => {
// ...
}
})
- run a callback whenever any error happens throughout the app
- great for services like Sentry, Rollbar, etc
Error Handling
alternatively use nuxt hook `vue:error`
export default defineNuxtPlugin((nuxtApp) => {
nuxtApp.hook('vue:error', (..._args) => {
console.log('vue:error')
})
})
Error Handling
Rendering an Error Page
// ~/error.vue
<script setup>
defineProps(["error"]);
</script>
<template>
Oh noes!
<pre>
{{ error }}
</pre>
</template>
👍 Great for show stopping errors
lives in root directory
accepts an error prop
Error Handling
Rendering an Error Page
// ~/error.vue
<script setup>
defineProps(["error"]);
</script>
<template>
Oh noes!
<button @click="clearError({ redirect: '/' })">
Go home
</button>
</template>
Call clear error with the redirect option to clear error and navigate away
Error Handling
The NuxtErrorBoundary Component
<template>
<!-- some content -->
<NuxtErrorBoundary @error="someErrorLogger">
<!-- You use the default slot to render your content -->
<template #error="{ error }">
You can display the error locally here.
<button @click="error = null">
This will clear the error.
</button>
</template>
</NuxtErrorBoundary>
</template>
Wrap portions of UI with NuxtErrorBoundary and if an error occurs anywhere within it, the error slot shows
Error Handling
Error related functions
- useError() - get the error currently being handled
-
throw createError() - create a new error and throw it
- on server - full-screen error page
- on client - throws a non-fatal error
- clearError() - clear the currently handled Nuxt error
Questions?
🙋
Exercise
7
Path to Migration
8
Migrate from 2 to 3
Throughout the workshop you've seen:
✅ Juicy new Nuxt 3 features
✅ differences in the old & new styntaxes

Migrate from 2 to 3
🎉 Now let's migrate!

Migrate from 2 to 3
⚠️ But first....
a warning

Setting expectations
Migrate from 2 to 3
Nuxt 3 is a complete rewrite of Nuxt 2
There will be significant changes when migrating a Nuxt 2 app to Nuxt 3
You WILL run into errors and have to do some googling when errors surface
Not all modules are ready for Nuxt 3. You might have to create temporary work arounds

Setting expectations
Migrate from 2 to 3
Don't worry
There are some tools available

Official Upgrade Guide
Migrate from 2 to 3

Nuxt Cheat Sheet
Migrate from 2 to 3

Debbie O'Brien Blog Post
Migrate from 2 to 3


2 options for Migrating
Migrate from 2 to 3
Straight to Nuxt 3
- Migrate all at once
- Start new Nuxt 3 proeject, and move files one at a time
- Progressively migrate
- Upgrade directly in existing project
- My experience hasn't been great
Nuxt Bridge
Progressively migrate with this compatibility layer for Nuxt 2
Nuxt Bridge
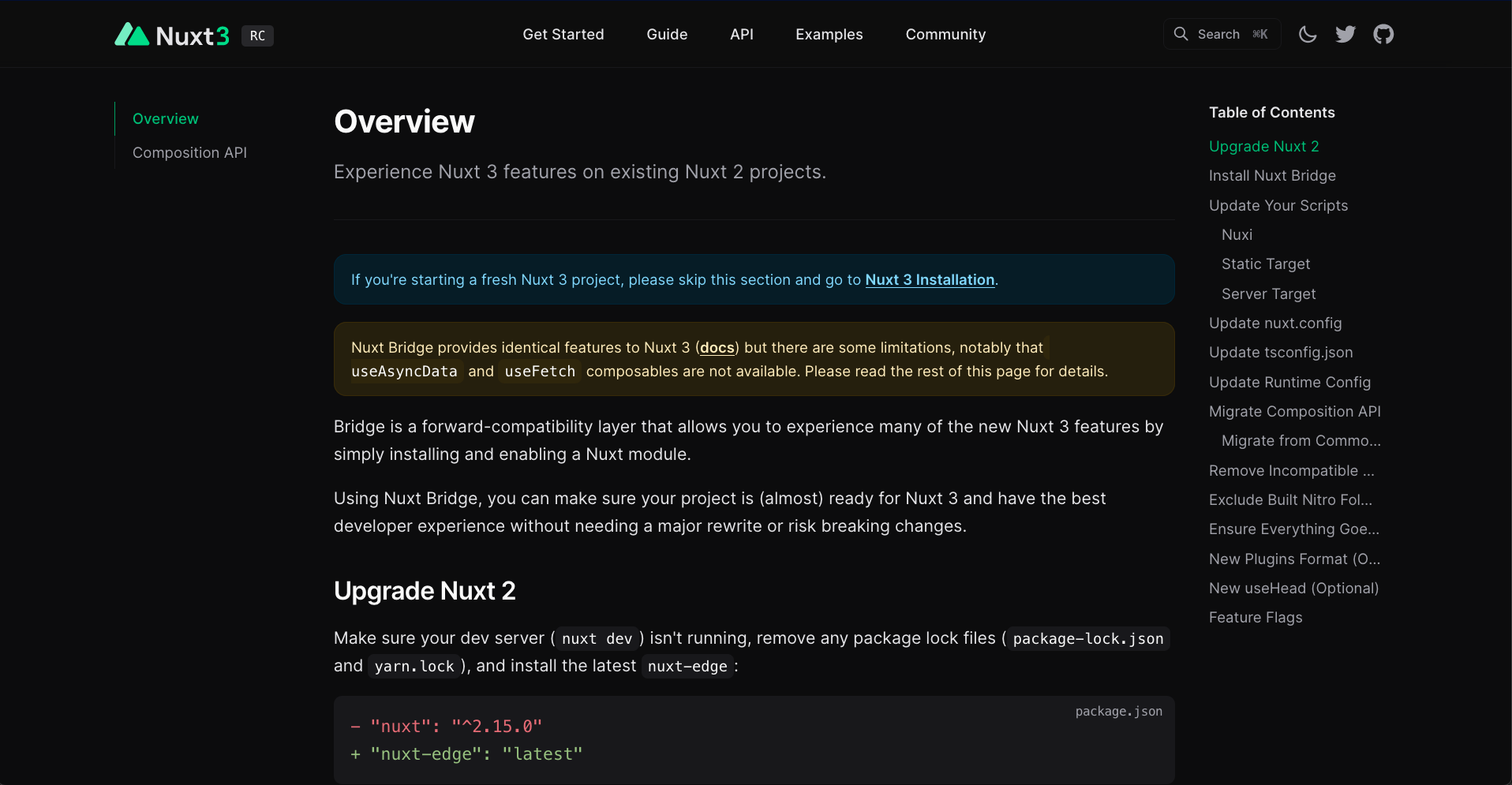
- Nitro
- Vite
- Composition API
- Script Setup
- Auto Imports

Migrate from 2 to 3
- You've been given the tools
- You know the majority of syntax changes
Let's give it a try!

Let's give it a try!
Migrate from 2 to 3
In the last exercise we'll:
- Start with an existing Nuxt 2 project
- Create a brand new Nuxt 3 project
- Move files over 1 at a time from Nuxt 2 project until working
Questions?
🙋
Exercise
8
Q&A
❓
Resources
Composition API


Resources
Composition API
Resources
Nuxt 3


Resources
Pinia
🙏
Thanks!



